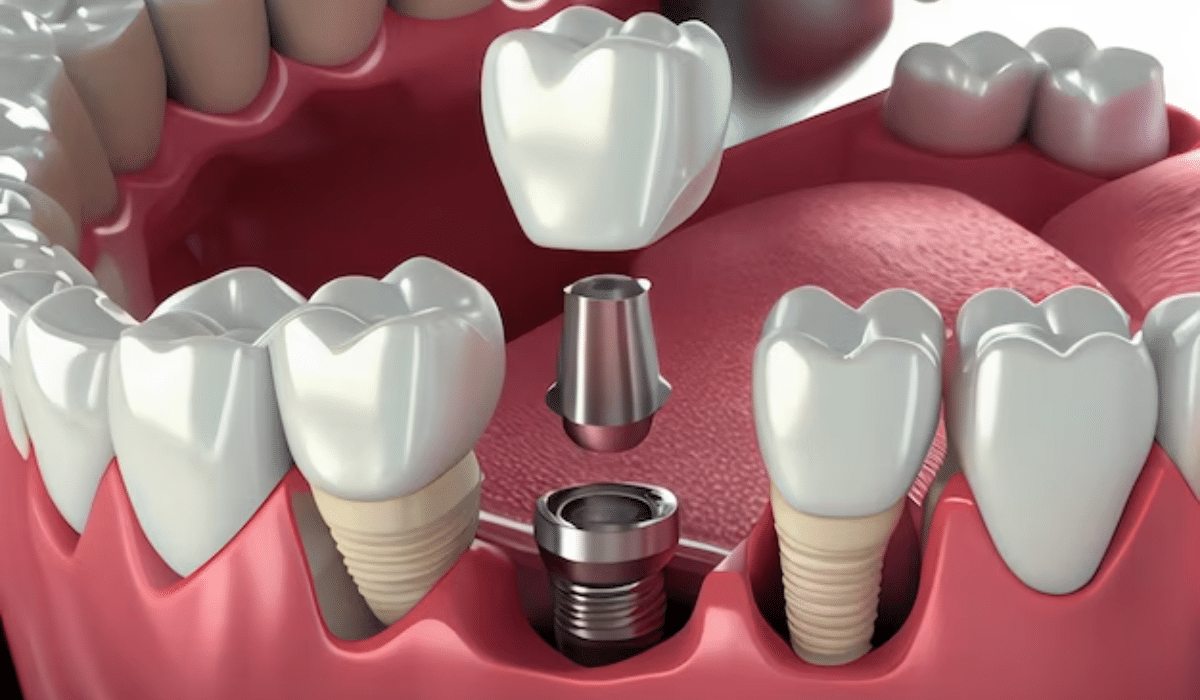
Dental implants are a popular and effective option for replacing missing teeth, offering numerous benefits for oral health and aesthetics. However, some potential side effects, like tinnitus, can arise after the procedure. This can raise concerns for individuals considering implants, leading them to wonder: “Can dental implants cause tinnitus?” This blog delves into the connection between dental implants and tinnitus. Also, the blog will explore the potential causes of this condition and offer insights for those seeking answers.
Understanding Tinnitus: The Ringing in Your Ears
Tinnitus, often referred to as “ringing in the ears,” is a condition where you perceive sound even though there’s no external source generating it. This phantom sensation can manifest in various ways, affecting individuals differently. Let’s delve deeper into understanding tinnitus:
A Spectrum of Sounds
- Beyond Ringing: While “ringing” is the most common description, tinnitus can encompass a wide spectrum of sounds. People may experience buzzing, whooshing, hissing, clicking, or even musical tones.
- Variations in Volume and Pitch: The perceived volume and pitch of tinnitus can also vary significantly. It can be a faint, barely noticeable whisper or a loud, intrusive roar that disrupts daily activities.
- Fluctuations and Persistence: The sound might be constant or come and go, appearing sporadically or lasting for extended periods. Sometimes, tinnitus can even pulsate in rhythm with your heartbeat.
Impact on Daily Life
While not always a severe medical condition, tinnitus can significantly impact your well-being. Here’s how:
- Difficulties Sleeping: The constant presence of sound can make it challenging to fall asleep and stay asleep, leading to fatigue and impacting overall health.
- Concentration and Focus: Tinnitus can be distracting, hindering your ability to concentrate on work, studies, or conversations.
- Emotional Toll: The frustration and stress caused by tinnitus can lead to anxiety, depression, and feelings of isolation.
Causes of Tinnitus
Tinnitus can arise from various factors, including:
- Noise-induced hearing loss: Exposure to loud noises over time can damage the delicate hair cells in the inner ear, leading to tinnitus.
- Earwax buildup: Excessive earwax can impede sound waves and contribute to tinnitus perception.
- Medications: Certain medications, like aspirin or some antibiotics, can have tinnitus as a side effect.
- Underlying medical conditions: In rare cases, tinnitus can be a symptom of an underlying medical condition, such as high blood pressure, head injury, or a tumor.
The Potential Link Between Dental Implants and Tinnitus
While dental implants are a well-established and generally safe method for tooth replacement, some individuals may experience temporary tinnitus, or ringing in the ears, following the surgery. While the exact cause-and-effect relationship remains under investigation, several factors might contribute to this occurrence:
Surgical Trauma
The implant placement procedure requires making precise incisions and drilling into the jawbone to create a secure foundation for the implant. Although performed with meticulous care, this process can potentially impact nearby anatomical structures, including the temporomandibular joint (TMJ). It is to be noted that the TMJ connects the jaw to the skull and delicate middle ear bones. Any unintentional, though minor, irritation or inflammation in these close-proximity structures can sometimes trigger temporary tinnitus.
Dental Equipment Vibrations
The surgical process utilizes specialized dental instruments that generate high-frequency vibrations. While these vibrations are generally controlled and contained within the surgical site, some individuals may be more sensitive to their effects. In these cases, the vibrations, particularly if prolonged or intense, have the potential to irritate the delicate structures of the inner ear, including the cochlea, which is responsible for converting sound waves into electrical signals for the brain. This irritation can sometimes manifest as tinnitus.
Individual Susceptibility
It’s important to recognize that individual susceptibility plays a significant role in the development of tinnitus. People with pre-existing conditions affecting the auditory system, such as hearing loss or Meniere’s disease, might be more prone to experiencing tinnitus after implant surgery.
Addressing Tinnitus After Dental Implant Surgery
While uncommon, tinnitus, a ringing or buzzing sensation in the ears, can occur after dental implant surgery. Here’s what you can do if you experience this:
Maintain Open Communication with Your Dentist
- Early Notification: Inform your dentist immediately about any tinnitus symptoms you experience following surgery. This allows them to address your concerns and assess the situation promptly.
– Detailed Description: Describe the tinnitus in detail, including:
– Type of sound: Is it ringing, buzzing, clicking, or whistling?
– Location: Is it in one ear or both?
– Volume: Is it constant, or does it come and go? How loud is it?
– Impact: Does it affect your hearing or daily life?
- Medical History: Share any relevant medical history, including ear infections, head injuries, or pre-existing tinnitus. This helps your dentist understand your risk factors.
Monitor and Document the Symptoms
- Track the Duration: Keep a record of how long you’ve experienced tinnitus. Is it temporary or persistent?
- Assess the Severity: Note the severity of the tinnitus. Does it fluctuate throughout the day? Is it mild or significantly impacting your sleep and daily activities?
- Maintain a Journal: Keeping a journal to document the details mentioned above can be helpful for monitoring changes. Also, it will help in providing valuable information to your dentist or other healthcare professional.
Explore Treatment Options (if necessary)
Consult a Specialist: If your tinnitus persists for longer than a few weeks or worsens, your dentist may recommend consulting an otolaryngologist (ENT specialist) who specializes in ear, nose, and throat conditions.
Understand the Cause: Determining the cause of your tinnitus is crucial for recommending appropriate treatment. While dental implant surgery may not directly cause tinnitus in most cases, it’s important to rule out any related complications.
Consider Treatment Options: Depending on the cause and severity of your tinnitus, various treatment options may be available, including:
- Sound therapy: Using masking sounds like white noise or nature sounds to help mask the tinnitus and make it less noticeable.
- Tinnitus retraining therapy: A form of sound therapy combined with counseling to help your brain habituate to the tinnitus and reduce its perceived loudness and annoyance.
Medications: In some cases, medications like antidepressants or anti-anxiety drugs might be prescribed to manage tinnitus-related anxiety or sleep disturbances.
Minimizing the Risk of Tinnitus: Comprehensive Strategies
Protect Your Ears from Loud Noise
- Limit exposure to high-intensity sounds: This includes activities like attending loud concerts, using power tools without ear protection, or listening to music or audio at excessively high volumes, especially through headphones or earbuds.
- Utilize proper ear protection: Wear earplugs or noise-canceling headphones when exposed to loud environments. Also, choose appropriate noise reduction ratings (NRR) for the specific environment.
- Practice safe listening habits: Gradually increase the volume of your music or audio, and avoid listening above 60% of your device’s maximum volume. Limit headphone usage, especially for extended periods.
Manage Underlying Medical Conditions
- Maintain healthy blood pressure: High blood pressure can contribute to tinnitus. Regularly monitor your blood pressure and work with your doctor to manage it effectively.
- Address earwax buildup: Excessive earwax buildup can sometimes worsen tinnitus symptoms. Consult your doctor for safe and proper earwax removal if needed.
- Treat ear infections promptly: Untreated ear infections can damage inner ear structures and increase the risk of tinnitus. Seek medical attention if you experience ear pain, drainage, or hearing loss.
- Manage stress effectively: Stress is a known trigger for tinnitus. Practice relaxation techniques like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing to manage stress levels.
Adopt Healthy Lifestyle Practices
- Maintain a balanced diet: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains nourishes your entire being, potentially contributing to a reduction in tinnitus severity.
- Limit stimulants and alcohol: Excessive caffeine, smoking, and alcohol can exacerbate tinnitus. Consider reducing or eliminating these substances to create a calmer internal environment.
- Prioritize adequate sleep: Aim for 7-8 hours of quality sleep each night. Adequate sleep is crucial for your overall well-being and can significantly improve how you perceive tinnitus symptoms.
Dental implants offer a reliable and long-term solution for replacing missing teeth. While it’s essential to be aware of potential side effects like tinnitus, it’s crucial to understand that implants themselves are not the direct cause. Temporary tinnitus after surgery is relatively common, and it usually resolves on its own. Open communication with your dentist and seeking professional support when needed can help address any concerns and ensure a successful dental implant experience.
Find out if you qualify for Implants.life dental implants in less than 2 min.
Click Here
Click Here